The dielectric constant the dielectric constant
ε, which shows how many times the force of interaction of two electric charges in a medium is less than in vacuum. In an isotropic medium, ε is related to the dielectric susceptibility χ by the relation: ε \u003d 1 + 4π χ. The dielectric constant of an anisotropic medium is a tensor. The dielectric constant depends on the field frequency; in strong electric fields, the dielectric constant begins to depend on the field strength.

Thanks to this modular system, users can save money throughout the entire product life cycle. Together with the ease of device selection and its easy-to-use wizard setup, the developers were especially interested in the accuracy of the measurement and the reliability of the sensors.
Versatile and very reliable. 
The user simply selects the appropriate version of the device and the necessary components for his task. Intelligent signal processing automatically detects changes in operating conditions and dynamically adapts them. This enables reliable overflow detection and level measurement even under very difficult conditions. The built-in memory stores the measured values, events and response patterns and identifies all important information about the operating conditions and the state of the sensor.
DIELECTRIC PERMEABILITY, dimensionless quantity e, showing how many times the force of interaction F between electric charges in a given medium is less than their interaction force F o in vacuum:
e \u003d F o / F.
The dielectric constant shows how many times the field is attenuated by the dielectric (cm. DIELECTRICS)quantitatively characterizing the property of an insulator to polarize in an electric field.
The value of the relative dielectric constant of a substance, characterizing the degree of its polarizability, is determined by the polarization mechanisms (cm. POLARIZATION). However, the value to a large extent also depends on the state of aggregation of the substance, since upon transitions from one state to another, the density of the substance, its viscosity and isotropy significantly change (cm. ISOTROPY).
Dielectric constant of gases
Gaseous substances are characterized by very low densities due to the large distances between the molecules. Due to this, the polarization of all gases is negligible and their dielectric constant is close to unity. The gas polarization can be purely electronic or dipole, if the gas molecules are polar, however, in this case, the electron polarization is of primary importance. The polarization of various gases is greater, the larger the radius of the gas molecule, and numerically close to the square of the refractive index for this gas.
The dependence of gas on temperature and pressure is determined by the number of molecules per unit volume of the gas, which is proportional to pressure and inversely proportional to absolute temperature.
At the air in normal conditions e \u003d 1,0006, and its temperature coefficient has a value of about 2. 10 -6 K -1.
The dielectric constant of liquid dielectrics
Liquid dielectrics can consist of non-polar or polar molecules. The value of e of nonpolar liquids is determined by electron polarization; therefore, it is small, close to the square of the refraction of light, and usually does not exceed 2.5. The temperature dependence of e of a non-polar liquid is associated with a decrease in the number of molecules per unit volume, i.e., with a decrease in density, and its temperature coefficient is close to the temperature coefficient of the volume expansion of the liquid, but differs in sign.
The polarization of liquids containing dipole molecules is determined simultaneously by the electronic and dipole-relaxation components. Such liquids have a higher dielectric constant, the greater the value of the electric moment of the dipoles (cm. DIPOLE) and the greater the number of molecules per unit volume. The temperature dependence in the case of polar liquids is complex.
Dielectric constant of solid dielectrics
In solids, it can take on a variety of numerical values \u200b\u200bin accordance with the variety of structural features of a solid dielectric. In solid dielectrics, all types of polarization are possible.
The smallest value of e are solid dielectrics consisting of nonpolar molecules and possessing only electron polarization.
Solid dielectrics, which are ionic crystals with a dense packing of particles, have electronic and ionic polarizations and have e values \u200b\u200bthat lie in a wide range (e of rock salt - 6; e corundum - 10; e rutile - 110; e calcium titanate - 150).
e of various inorganic glasses, approaching in structure to amorphous dielectrics, lies in a relatively narrow range from 4 to 20.
Polar organic dielectrics have a dipole-relaxation polarization in the solid state. e of these materials to a large extent depends on the temperature and frequency of the applied voltage, obeying the same laws as dipole liquids.
Technical advances and production technologies present new requirements for industrial measurements. Quick function settings allow the user to make all the necessary settings in a few simple steps. Built-in diagnostics, quick service and quick service are possible, and self-training for signal processing ensures stable operation without maintenance.
It ensures the safety and reliability of measurements in production systems in all sectors. This non-contact radar level sensor is suitable for continuous measurement of water level. This is a radar level meter of a lower price category, developed specifically in the field of water resources management. But it can also be used in many other tasks in a wide variety of industries.
Relative permittivity
Relative dielectric constant medium ε is a dimensionless physical quantity characterizing the properties of an insulating (dielectric) medium. Associated with the polarization effect of dielectrics under the action of electric field (and with the value of the dielectric susceptibility of the medium characterizing this effect). The value ε shows how many times the force of interaction of two electric charges in the medium is less than in vacuum. The relative dielectric constant of air and most other gases under normal conditions is close to unity (due to their low density). For most solid or liquid dielectrics, the relative permittivity ranges from 2 to 8 (for a static field). The dielectric constant of water in a static field is quite high - about 80. Its values \u200b\u200bare great for substances with molecules that have a large electric dipole. The relative permittivity of ferroelectrics is tens and hundreds of thousands.

What are the benefits of radar level meters in the water sector? The measurement is not affected by temperature, wind, fog or rain. You can even measure a low foam environment due to its much higher sensitivity compared to ultrasonic sensors. In particular, when measuring the flow through open channels, the level of measuring the radar level is many times more accurate than the ultrasonic sensor, since the activity of the ultrasonic sensor greatly affects the temperature, and the sensor on which the sun is illuminated can reach 20% error.
Measurement
Relative permittivity of a substance ε r can be determined by comparing the capacitance of the test capacitor with a given dielectric (C x) and the capacitance of the same capacitor in vacuum (C o):
Practical use
The dielectric constant of dielectrics is one of the main parameters in the development of electric capacitors. The use of materials with high dielectric permittivity can significantly reduce the physical dimensions of capacitors.

This unit is equipped with six relay outputs and has all the necessary properties for pump control and flow measurement. It has a built-in counter to measure the total amount of waste. The user can display the measured value in units that suit him, and can also display the total amount of protection.
This kit is the ideal solution for most water management tasks. The flow measurement is based on the principle of ultrasonic wave propagation through the flow medium - the time difference between the transmission and reception of the ultrasonic signal, the change in its frequency or phase shift is estimated.
The capacitance of the capacitors is determined by:
where ε r the dielectric constant of the substance between the plates, ε about - electric constant S is the area of \u200b\u200bthe capacitor plates, d - the distance between the plates.
The dielectric constant is taken into account when designing printed circuit boards. The value of the dielectric constant of the substance between the layers in combination with its thickness affects the value of the natural static capacity of the power layers, and also significantly affects the wave resistance of the conductors on the board.
There is no need to destroy the pipe wall and no need to close the production process during assembly. There is no pressure loss at the measurement point. No parts of the flowmeter are in contact with the medium. The ultrasonic flow meter responds quickly to sudden changes in flow, providing reliable and accurate measurement even in adverse conditions. An advantage is also the security aspect. In the case of hazardous devices, the installation of all conventional contact flow meters must be approved.
Underground storage of natural gas
However, ultrasonic flow meters usually do not require this. Underground gas storage can be created in exhaust manifolds from natural gas, in caves from underground salt formation, etc. each underground gas storage has its own characteristics determined by the type of storage, but everyone faces similar problems: high dynamic bidirectional gas flow under high pressure, significant moisture content in the extracted gas, which must be dried before reaching the transport network, the need to prevent hydrate formation, frequent decrease or increase in gas pressure.
Frequency dependent
It should be noted that the dielectric constant is largely dependent on the frequency electromagnetic field. This should always be taken into account, since the reference tables usually contain data for a static field or low frequencies up to several kHz units without indicating this fact. At the same time, there are also optical methods for obtaining relative permittivity from the refractive index using ellipsometers and refractometers. The value obtained by the optical method (frequency 10 14 Hz) will significantly differ from the data in the tables.
Wellhead gas flow measurement

Depending on the type of storage, significant pressure can be created during gas injection and extraction. The traditional way of measuring the gas flow through the aperture and the pressure difference under these conditions is neither accurate nor reliable. Since these flowmeters are limited by adjustability, they usually operate in a so-called cascade method to cover a sufficiently wide range of flow rates. This leads to large pressure losses. They are also subject to significant wear. At low pressure, pressure gauges can be impregnated with hydrate or dirt.
Consider, for example, the case of water. In the case of a static field (the frequency is zero), the relative permittivity under normal conditions is approximately 80. This is true up to infrared frequencies. Starting at about 2 GHz ε r starts to fall. In the optical range ε r is approximately 1.8. This is consistent with the fact that in the optical range the refractive index of water is 1.33. In a narrow frequency range, called optical, the dielectric absorption drops to zero, which actually provides a person with a vision mechanism in an earthly atmosphere saturated with water vapor. With a further increase in the frequency, the properties of the medium change again. The behavior of the relative permittivity of water in the frequency range from 0 to 10 12 (infrared) can be read in
This leads to excessive maintenance costs and the need for frequent shutdowns. Simply put, measurements outside the pipeline clearly show that this is a much more convenient solution for measuring flow in this case. Since the flow meters do not come in direct contact with the gas flowing inside the pipeline, they are not affected by the flow of solids, humidity or high humidity. In addition, the measurement of non-invasive gas flow does not cause pressure loss and, therefore, does not adversely affect energy efficiency.
Notes
see also
- Dielectric constant of vacuum (electric constant)
Dielectric constant values \u200b\u200bfor some substances
| Substance | Chemical formula | Measurement conditions | The characteristic value of ε r |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Al | 1 kHz | -1300 + 1.3 · 10 14 i |
| Silver | Ag | 1 kHz | -85 + 8 · 10 12 i |
| Vacuum | - | - | 1 |
| Air | - | Normal conditions, 0.9 MHz | 1,00058986 ± 0.00000050 |
| Carbon dioxide | CO 2 | Normal conditions | 1,0009 |
| Teflon | - | - | 2,1 |
| Nylon | - | - | 3,2 |
| Polyethylene | [-CH 2 -CH 2 -] n | - | 2,25 |
| Polystyrene | [-CH 2 -C (C 6 H 5) H-] n | - | 2,4-2,7 |
| Rubber | - | - | 2,4 |
| Bitumen | - | - | 2,5-3,0 |
| Carbon disulphide | CS 2 | - | 2,6 |
| Paraffin | C 18 H 38 - C 35 H 72 | - | 2,0-3,0 |
| Paper | - | - | 2,0-3,5 |
| Electroactive Polymers | − | − | 2-12 |

 Car generator and how to check it
Car generator and how to check it Safe use of household electrical appliances
Safe use of household electrical appliances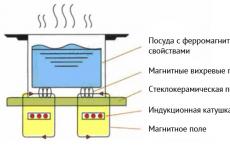 Economical Electric Cookers
Economical Electric Cookers